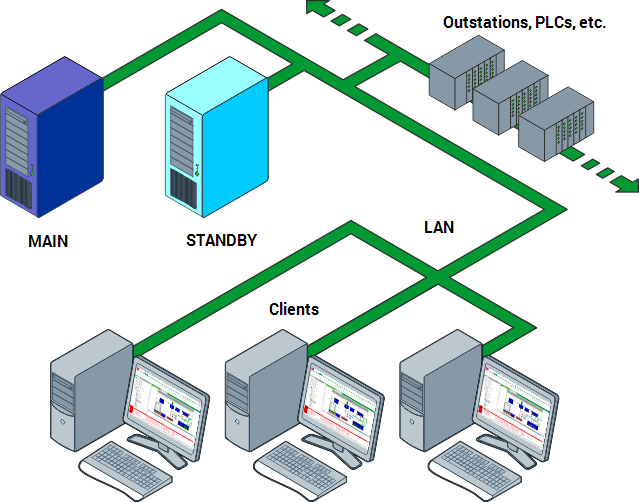
A Hot-Standby Pair architecture uses two servers to provide redundancy and allow for load sharing.
Multi-server systems (redundancy) require a license and so are only supported by full versions of ClearSCADA.
In a Hot-Standby Pair, one server acts as the Main server and the other server acts as a Standby server. The Main server runs the system drivers and acts as the primary server whereas the Standby server is used as a backup server.

During synchronization, the Main server updates the Standby server. This process provides the Standby server with data and configuration that accurately represents the data on the Main server
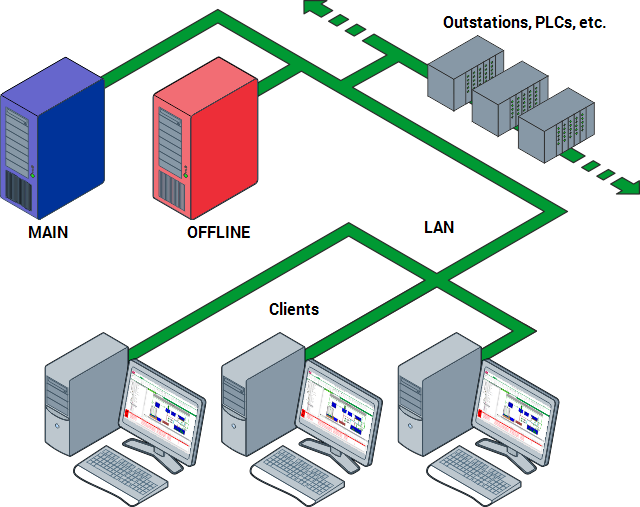
When an offline server is able to resume normal operations, it communicates with the other server (which is now Main) and becomes the Standby server.
If the Standby loses its connection with the Main server, a Main-Main situation can occur. This is when both servers act as Main servers because they cannot communicate with each other.
ATTENTION: If an offline Main-Standby connection is recovered, and the server that was originally Main is restored as the Main server, the data reported while the Standby server was Main may be lost. For example, if Server A has been Main for 10 hours when the connection is lost, Server B switches to Main. The connection to Server A is restored within 2 hours, and as Server A has been Main for longer than Server B (in total), it is set to Main and Server B is switched to Standby. The data that was reported to Server B while it was Main may be lost. If Duty-Duty support is enabled, the data will be merged (see Enable or Disable Duty Mode), otherwise the data is only retrievable if the outstations or PLCs being used support Windback. For more information, refer to the documentation for your outstations, PLCs etc.
To set up a Hot-Standby Pair architecture, see Configure a Hot-Standby Pair.