Permanent Standby servers can only be set to Standby and are used as an additional part of a Hot-Standby Pair or Triple Standby architecture. Also known as ‘Corporate Servers’, Permanent Standby servers can reduce the demand placed on the Main and Standby servers in a multi-server architecture.
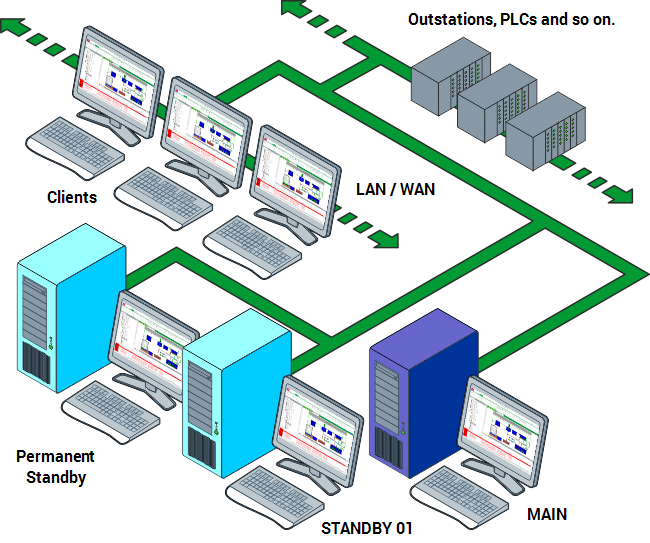
A Permanent Standby server can be used:
- As a ‘performance firewall’—clients can connect to the system via the Permanent Server instead of the Main or Standby server, which reduces the demand on the Hot-Standby Pair’s resources.
- To improve performance for clients. This applies to read operations where the clients would have to connect to the Standby server over a slow WAN. Instead of reading data from the Standby server, the clients can be connected to the Permanent Standby locally—they can read the data from the Permanent Standby instead of the Standby and so avoid the need to use the WAN.
- To increase the amount of historic data that is available online. By configuring a Permanent Server to store more historic data online, you can increase the amount of historic data that is available online without affecting the Main and Standby server’s resources. For example, a Permanent Standby server can be configured to store historic data online for 5 years while the Main and Standby servers can be configured to store historic data online for only 1 year.
It is also possible to configure clients so that they connect to the Permanent Standby in preference to the other servers (they will only connect to the Main or Standby server if the Permanent Standby server is offline). To achieve this, you simply need to configure the client connection to the Permanent Standby server to have a lower cost than the cost settings for the connections to the Main and Standby servers
ClearSCADA allows you to connect up to four Permanent Standby servers to a Hot Standby Pair architecture or up to three Permanent Standby servers to a Triple Standby architecture. Typically, a system that uses Permanent Standby servers is set up as follows:
- Clients that are used by operators and engineers are connected to a Hot-Standby Pair or Triple Standby architecture. As these are the users that use the system to monitor and control plant, they need to have a larger amount of system resources available so that they can react quickly and efficiently to ‘real-life’ situations on site.
- Clients that are used by managers, administrators and analysts are connected to a Permanent Standby server. This provides access to the data on the system without placing a high demand on the resources of the Main and Standby servers. So managers, administrators and analysts can access the system data and statistics without affecting the load on the Main and Standby servers.
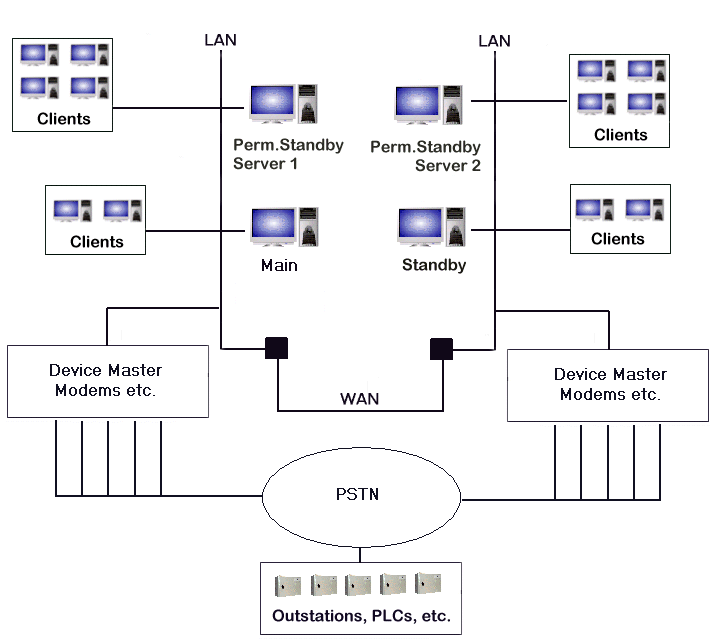
In the setup shown in the following diagram, two Permanent Standby servers are used to reduce the load on the Main server and Standby server. The load is reduced by having the majority of users access the system via the Permanent Standby servers with fewer users accessing via the Main and Standby servers.
On some systems, Permanent Standby servers are also used to store large amounts of historic data. This is an effective way of making data available to users without using the resources of the Main and Standby servers.
A Permanent Standby server that is used in a Triple Standby architecture can only connect to two of the three Main/Standby servers. For more information, see Configure Triple Standby.
Multi-server systems (redundancy) require a license and so are only supported by full versions of ClearSCADA.
To set up a multi-server architecture that uses one or more Permanent Standby servers, see the topics that are listed in the gray footer section at the bottom of this topic. Select the relevant entry to display the topic that you require.