Use the Current value is instantaneous ROC check box on the State tab of the Rate of Change Accumulator Form to specify when the Rate of Change value increments:
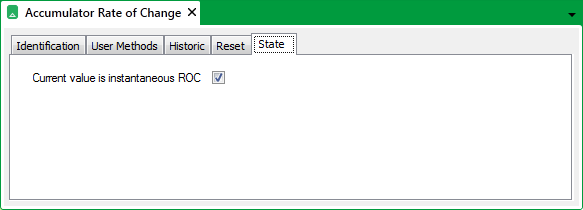
Select the Current value is instantaneous ROC check box for Geo SCADA Expert to calculate the Rate of Change between the present source value and the previous source value.
Example:
The ‘Current value is instantaneous ROC’ check box is selected for a Rate of Change Accumulator.
The Accumulator’s source changes in value from 14 to 24 over a five-second period. This produces an Accumulator value of 2.
(The value of the Accumulator is the difference between the present and previous source values (24 - 14), divided by the time (5)).
Clear the Current value is instantaneous ROC check box for Geo SCADA Expert to calculate the Rate of Change using Linear Regression. Linear Regression uses a statistical calculation to produce a ‘best fit’ straight line to the rate of change source data. This provides an estimate of the rate of change over the calculation period, with Geo SCADA Expert adjusting the resulting straight line as it processes new source data.
Example:
Two Rate of Change Accumulators are used to calculate the rate of change of an Analog point. A Trend is used to monitor the Analog and Accumulator values.
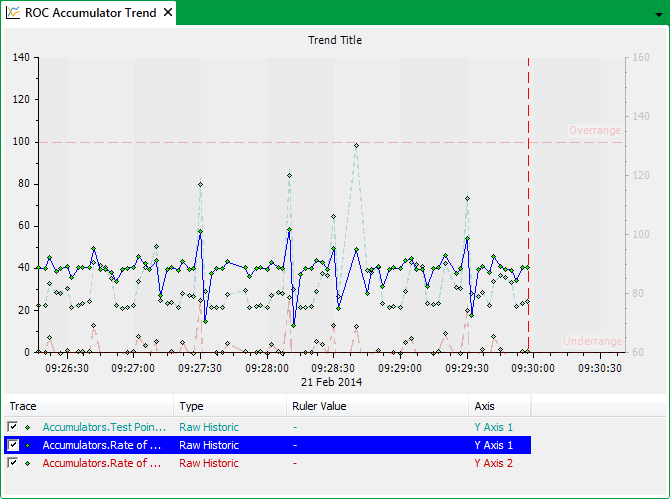
In the Trend shown above, the Analog point trace is attached to the left y-axis and the Rate of Change Accumulator traces to the right y-axis. The Accumulator values increase whenever the Analog value rises, and decrease whenever the Analog values falls, indicating the rate of change in the Analog point value.
The Accumulators use different types of calculation to evaluate the Analog point’s rate of change—one Accumulator calculates the difference between the previous and present Analog values and divides this by the time between the changes in value; the other Accumulator uses Linear Regression to evaluate the Analog point’s rate of change.