De-Militarized Zone (DMZ) Permanent Standby servers are servers that are used as an additional part of a Hot-Standby Pair or Triple Standby architecture. Like 'normal' Permanent Standby servers, they can only be set to Standby and cannot switch to Main. However, they have one key difference to 'normal' Permanent Standby servers—DMZ servers have no connection back to the system, and so cannot write to the system. This means that DMZ Permanent Standby servers offer more protection against malicious attacks, as they cannot be used to write data or interfere with the ClearSCADA database. Another benefit is that as there is no connection back to the system, it makes the configuration of a firewall between the system and the DMZ Permanent Standby server a much simpler task.
As DMZ Permanent Standby servers are unable to write to the ClearSCADA database, they cannot be used to change passwords. If a user’s password expires, they will need to define a new password on a non-DMZ server.
If the DMZ Permanent Standby server uses an Active Directory connection, then it can be used to change passwords that are also used within ClearSCADA. However, users cannot be created automatically by logging on to a DMZ Permanent Standby with an Active Directory connection.
DMZ Permanent Standby servers are only able to provide read-only access to clients. Any clients that connect to ClearSCADA via a DMZ Permanent Standby server can be used to display data, but cannot be used to perform controls etc.
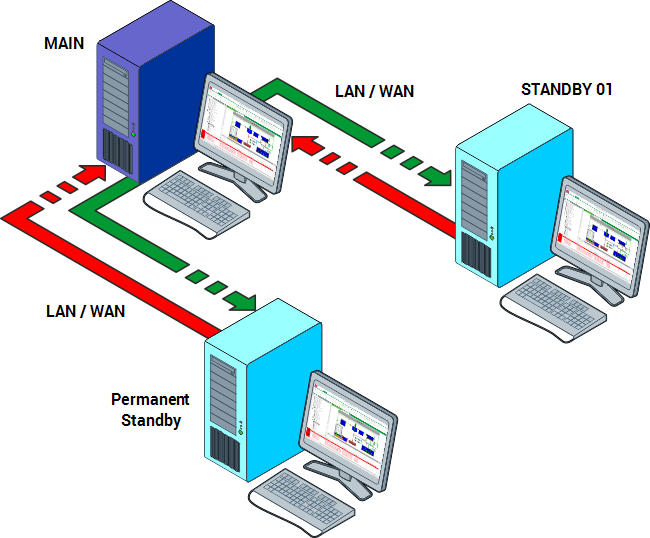
With a 'normal' Permanent Standby server, the Permanent Standby server can send data to, and receive data from the Main and Standby servers.
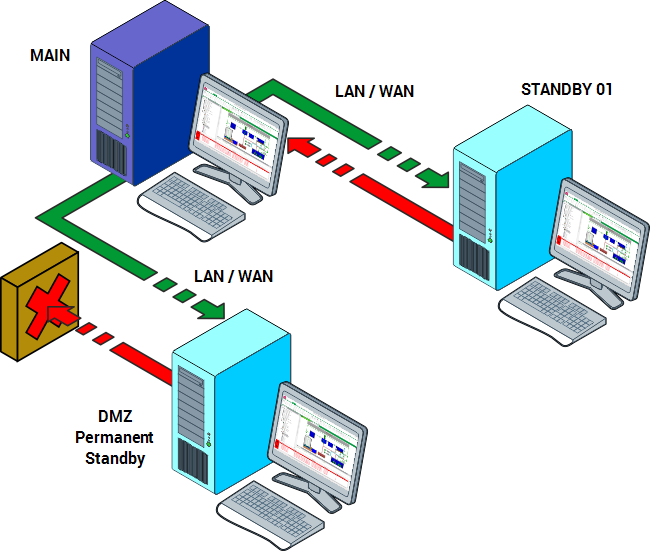
With a DMZ Permanent Standby server, the DMZ Permanent Standby server can only receive updates from the Main server (as part of the synchronization process). Any read requests are handled locally by the DMZ server itself, based on the information it has received from the Main server.
As with normal Permanent Standby servers, DMZ Permanent Standby servers can be used:
- As a ‘performance firewall’—clients can connect to the system via the DMZ Permanent Server instead of the Main or Standby server, which reduces the demand on the Hot-Standby Pair’s resources. However, the clients will only provide read access to the system data; they cannot be used to perform controls as the DMZ Permanent Standby server cannot write to the system.
- To improve performance for clients. This applies to read operations where the clients would have to connect to the Standby server over a slow WAN. Instead of reading data from the Standby server, the clients can be connected to the DMZ Permanent Standby locally—they can read the data from the DMZ Permanent Standby instead of the Standby and so avoid the need to use the WAN.
- To increase the amount of historic data that is available online. By configuring a DMZ Permanent Server to store more historic data online, you can increase the amount of historic data that is available online without affecting the Main and Standby server’s resources. For example, a DMZ Permanent Standby server can be configured to store historic data online for 5 years while the Main and Standby servers can be configured to store historic data online for only 1 year.
ClearSCADA allows you to connect up to four DMZ Permanent Standby servers to a Hot Standby Pair architecture or up to three DMZ Permanent Standby servers to a Triple Standby architecture. Typically, a system that uses DMZ Permanent Standby servers is set up as follows:
- Clients that are used by operators and engineers are connected to a Hot-Standby Pair or Triple Standby architecture. As these are the users that use the system to monitor and control plant, they need to have a larger amount of system resources available so that they can react quickly and efficiently to ‘real-life’ situations on site.
- Clients that are used by managers, administrators and analysts are connected to a Permanent Standby server or a DMZ Permanent Standby server. This provides access to the data on the system without placing a high demand on the resources of the Main and Standby servers. So managers, administrators and analysts can access the system data and statistics without affecting the load on the Main and Standby servers. Users that connect to the system via a DMZ Permanent Standby server cannot perform controls and other ‘write’ actions.
A DMZ Permanent Standby server that is used in a Triple Standby architecture can only connect to two of the three Main/Standby servers. For more information, see Configure Triple Standby.
Multi-server systems (redundancy) require a license and so are only supported by full versions of ClearSCADA.
To set up a multi-server architecture that uses one or more DMZ Permanent Standby servers, refer to the following section: