This section applies to advanced drivers only.
Drivers detect that the server's clock has changed by comparing the server's real-time clock (RTC) with the CPU ticker. If a difference is detected, it means that the clock has changed, and so the driver will update its internal timers accordingly. It will also set the outstation clocks to the new time.
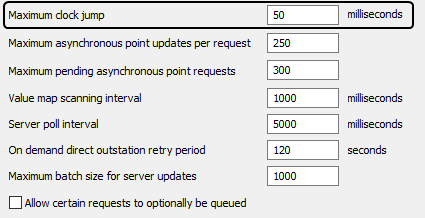
The threshold on the difference between the RTC and the CPU ticker is defined by the Maximum Clock Jump setting. Any difference above this threshold is treated as a change to the clock.
The clocks in some servers can cause significant differences between the clock and ticker. These differences are referred to as jitter. To allow for the amount of jitter, you may need to increase the Maximum Clock Jump threshold.
The default setting of 50 milliseconds is often sufficient, but some servers may need a higher setting (possibly as high as 250ms).
To define the maximum permitted time difference between the server clock and CPU ticker:
- Access the ClearSCADA Server Configuration Tool (see Accessing the ClearSCADA Server Configuration Tool).
- Expand the Global Parameters branch of the tree-structure.
- Select Drivers.
- In the Maximum Clock Jump field, enter the threshold for the difference between the RTC and the CPU ticker (that indicates the clock has changed).
-
- Right-click on the system icon in the tree-structure, and select the Apply Changes option to apply the changes.
- Restart the required driver(s) so that the new timeout(s) take effect (main server only). For more information, see Start and Stop a Driver.
- Repeat steps 2-6 inclusive for the other servers in the system, except permanent standby servers.