You can create single-layer maps or multi-layer composite maps in ClearSCADA, from online or offline mapping sources, which you can then use for a variety of purposes. For example, you can display:
- The geographic location of items in the ClearSCADA database
- Geographic information, such as weather data.
ClearSCADA maps have one or more layers. There are two types of map layer, as follows:
- Base layer. The base layer of a map provides the framework onto which you can display geographic information. The base layer provides the geographical context for the information you want to display on a map and for the story that you want your map to tell. Typically, although not necessarily, base layer maps are of a specific geographic region (for example, a map of Europe)
- Overlay layers. These are map layers which appear on top of the base layer map. Overlay layers provide the essential content of your map (for example, weather information). They tell the story that you want your map to tell. Overlay layers show the relationship between features and data that relate to and occupy the same geographical space. They help users to identify the spatial association or connection between features and information.
In ClearSCADA, you can display a base layer map as a standalone map (for example, to use as a framework to display the location of a database item) or you can create maps which have a base layer and one or more overlays. You can also create maps which offer a user a choice of base layer and a choice of overlays to display.
For example, a base layer map could be a map of Europe, which might look like this:
You could either display this map as a standalone map or you could overlay this base layer map with rainfall data, as follows:
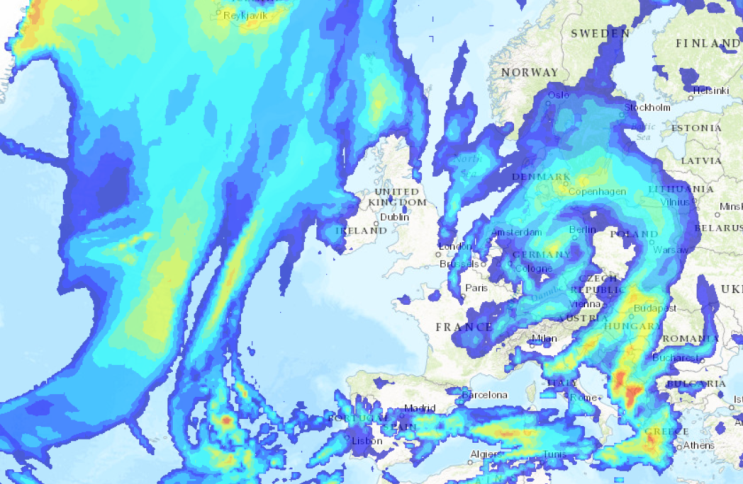
To create a map, you need to specify which layers will make up your map, and specify the sources of these layers (these can be online or offline sources). For more information, see Creating a ClearSCADA Map.
Once you have created a map, you can then display it in ClearSCADA (see Displaying a ClearSCADA Map).
When users display ClearSCADA maps, they can zoom in and out to see more or less detail. Users may also have a choice of base and overlay layers to view (see Using a ClearSCADA Map).