Add and Configure the Entries in an IP Routing Table
You use a SCADAPack x70 IP Routing Table to specify the IP routing that a particular SCADAPack x70 device is to use in order to connect to a commercial TCP/IP network. You use the table to specify the packet forwarding and IP gateway services that are required to enable such functionality. You can specify up to 20 static IP routes per IP Routing Table.
Where TCP/IP packets are routed through the SCADAPack x70 device, IP routes may or may not be needed depending on the Disable IP Forwarding configuration (see Enable or Disable IP Forwarding):
- Where IP Forwarding is enabled, there is no need to include an IP Routing Table entry for IP addresses that are on the same local subnet as a SCADAPack x70 device interface. Data packets will be automatically forwarded to those addresses.
- Where IP Forwarding is disabled, IP routes are required for communication between SCADAPack x70 device interfaces, even if the IP address for a device is on the same local subnet as a SCADAPack x70 interface.
Where the SCADAPack x70 device is directly communicating using an IP address in the same local subnet as one of its interfaces, an IP route is not required, regardless of the Disable IP Forwarding configuration.
Where IP route entries are added with overlapping subnets, the IP route entry with the narrowest subnet is the entry used to route the data packet. This establishes a selection priority among multiple IP routes. Where multiple routes could be applied to the same IP address, the route to be used is chosen in the following order:
- Host route (subnet mask 255.255.255.255).
- Narrowest subnet Network route (for example, subnet mask 255.255.255.252).
- Gateway route (where a gateway IP is configured on the route).
communication loss
The entries that you specify in an IP Routing Table are persistent (that is, they are retained when the SCADAPack x70 device restarts).
In the Geo SCADA Expert database, the table is built into the SCADAPack x70 Device Configuration item to which it relates. Changes made to the routing configuration are downloaded to the SCADAPack x70 device when that device's Download Configuration pick action is next executed.

You specify these properties for each route in a SCADAPack x70 IP Routing Table:
The IP address of the device or sub-network in the remote network to which the SCADAPack x70 device is to transmit TCP/IP packets. Use the Destination Address in conjunction with the Subnet Mask to identify either a single host address, or a range of target host IP addresses.
192.186.1.0
Used in conjunction with the Destination Address to identify either a single host address, or one of a range of host addresses (a subnet) to which the SCADAPack x70 device is to transmit TCP/IP packets.
255.255.255.0
The physical port on the SCADAPack x70 device via which that device is to transmit the TCP/IP packets.
When adding or editing a route, you use a combo box to select the required port. The options that are available vary, depending on the model of SCADAPack x70 device and its configuration, but might include Ethernet Port and/or Serial Port entries.
Serial Port options are only available if the SCADAPack x70 device has one or more serial ports on which the Port Function is set to 'PPP/TCPIP' (see Device Configuration Serial Port Tabs).
The IP address of the host that provides the ‘gateway’ to the target host.
192.168.0.1
The Gateway IP Address should be on the same subnet as the SCADAPack x70 device’s interface for the corresponding route. For example, if the Ethernet 1 interface is configured with an IP address of 192.168.0.1 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, the gateway address could be 192.168.0.2, but should not be 192.169.0.1
Defines the route priority, or cost, of an interface when multiple paths exist for interconnecting IP Hosts. The higher the number, the lower the priority. Set the entry to zero to apply the default metric value ('cost') for a particular type of route. Generally, PPP interfaces tend to have a higher metric, and therefore a lower priority, than Ethernet interfaces.
- Display the Table for the relevant SCADAPack x70 Device Configuration item.
- Select the IP Routing Table tab to display the IP Routing Table.
- Select the Add IP Route button.
The Add IP Route Entry dialog box is displayed.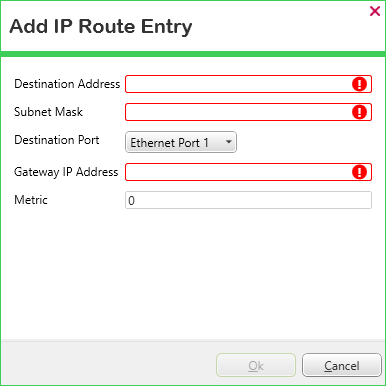
- Populate the fields as required (see above).
The fields that are highlighted indicate those that need populating with a value that has to take a specific format, as opposed to fields to which a default value is already assigned. The highlighting is removed once the field is populated with a value that has the required format.
- Select the OK button to close the dialog box and add the entry to the table.
- Display the Table for the relevant SCADAPack x70 Device Configuration item.
- Select the IP Routing Table tab to display the IP Routing Table.
- Either:
- Double-click on the entry that you want to edit.
Or:
- Click on the route that you want to edit.
- Select the Edit IP Route button.
The Edit IP Route Entry dialog box is displayed.
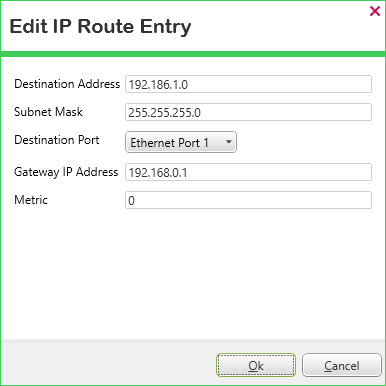
- Change the route's configuration as required.
- Select the OK button to confirm the changes, close the dialog box, and update the Routing Table.
- Display the Table for the relevant SCADAPack x70 Device Configuration item.
- Select the IP Routing Table tab to display the IP Routing Table.
- Select the entry for the route that is no longer required.
- Select the Remove IP Route button. (The button is only available for use when an entry is selected in the table.)
The route that was highlighted is removed from the table.
- Click on the column heading by which you want to sort the entries in the table. (To reverse the sorting order, click on the same column heading again.) The order in which the entries are sorted does not impact on the routing functionality.
When you redisplay the table, the entries are listed in the order in which they were added to the table.