You can use the Miscellaneous tab to configure the following settings for the server:
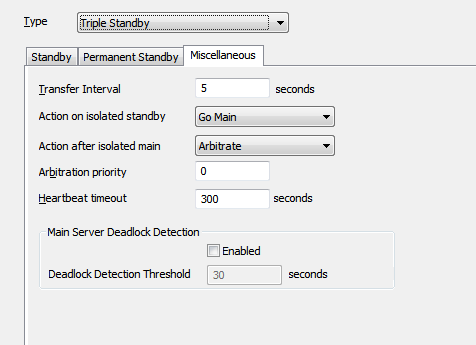
Define how often ClearSCADA attempts to update the servers in the server arrangement (Hot-Standby Pair, Triple Standby, etc.). If you need to define different update intervals for the servers, perhaps due to different connection speeds, you can achieve this by using the Interleave setting on the Standby (or Permanent Standby) tab. For more information, see Define the Transfer Interval and Transfer Timeouts.
ATTENTION: Leave the default Transfer Interval setting of 5 in place unless a Schneider Electric engineer instructs you to make a change. Incorrect use of the Transfer Interval setting can cause slow system performance.
Define what action a Standby server should take if it loses its connection to the other server(s). For more information, see Define what Action Should be Taken when a Server Becomes Isolated.
Define what action a server should take after a network connection is restored to an isolated Main server. For more information, see Define what Action Should be Taken when a Server Becomes Isolated.
Define whether the server becomes Main in preference to other servers in Main-Main or Main-Main-Main situations (see Define the Server’s Arbitration Priority).
Define the maximum amount of time for which no activity from the remote server will indicate a lost connection. ClearSCADA will use this timeout to determine if there is complete inactivity on a link. If there is complete inactivity, ClearSCADA will shut down the link (see Multi-Server Connection Poll Requests).
Do not confuse this Heartbeat Timeout field with the Heartbeat Timeout field that appears on the Standby tab of the Partners settings.
The Heartbeat Timeout property on the Miscellaneous tab is the TCP heartbeat interval, used to check whether the TCP connection to the remote end is still connected. The property detects whether the remote end has closed and whether ClearSCADA has received notification to that effect (if it has not, this could indicate that the underlying transport has failed).
The Heartbeat Timeout property on the Standby tab is a ClearSCADA application polling mechanism that is used to determine the state and status of the remote ClearSCADA server (see Define the Monitor Timeout Settings for a Server).
Main Server Deadlock Detection
The Main Server Deadlock Detection section allows you to enable and configure the monitoring of the database for the occurrence of a prolonged database deadlock event on the server currently acting as the MAIN.
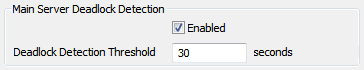
Select this check box to enable monitoring of deadlock events in the database. Clear the check box if you do not require monitoring.
When you enable monitoring enter the threshold time in seconds for a database deadlock event. In a Hot-Standby system the Standby servers will detect when the event exceeds the threshold time and a changeover will occur with one of the Standby servers becoming the MAIN see Main-Standby Changeovers and System Architectures).
If the deadlocked server recovers then the servers will perform MAIN-MAIN arbitration and the server may revert to being the MAIN or remain a Standby server (see Define the Server’s Arbitration Priority).
If the deadlocked server remains deadlocked it will require the intervention of an Administrator to restore its function.
You can use the Main Server Deadlock Detection feature in conjunction with, or independently of, the Database Watchdog feature. The latter feature can be used to detect whether the server has remained frozen for longer than a configurable amount of time, and if so, stop the server process and generate a minidump file that can be used to help analyze the cause (see Configure the Database Watchdog Settings).