Create the Content for a Property Translation Table
You create the content for a Property Translation Table outside of Geo SCADA Expert. The content has to take the form of a TSV (tab-separated values) file. Each entry in the file has to comprise a key/value pair that together forms a 'Property Set'. Each entry has to be in the format:
<Property Set Key>\t<Geo SCADA Expert Class>\t<Geo SCADA Expert Property Name>\n
Where:
<Property Set Key>is the key that represents the name of a property in a PropertySet that you want to map to a configuration property of an MQTT Sparkplug™ B Point in the Geo SCADA Expert database. The key and PropertySet have to exist in the Sparkplug birth certificate that Geo SCADA Expert will receive for the EoN Node or Sparkplug B Device.\tinserts a horizontal tab to separate the elements in a single entry.<Geo SCADA Expert Class>is the database class of the type of MQTT Sparkplug B point, or a base class of that point. This identifies the Class in which the configuration property is located in the Geo SCADA Expert database.<Geo SCADA Expert Property Name>is the relevant configuration field in the above database class. The field has to be writable. (Reference, Index, and Read Only fields in the Database Schema are not supported.)\ninserts a line feed and denotes the end of a single entry in the file.
You use the Database Schema in Geo SCADA Expert to ascertain the name of each <Geo SCADA Expert Class> and <Geo SCADA Expert Property Name> that you require. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the Database Schema and its structure before attempting to produce the content for a Property Translation Table file. For more information, see Welcome to the Guide to the Database, along with Understanding the Database and Working with the Database Schema. You also have to be familiar with the PropertySet keys, values, and data types of the metrics that you intend mapping to equivalent configuration fields of MQTT Sparkplug B Points in the Geo SCADA Expert database.
Be aware of the following:
-
You cannot include a Property Translation Table in a Group Template. However, if you intend using Group Templates and Group Instances, you can initially use a 'normal' Group that you later convert into a Group Template (see Preparation).
-
Do not include any blank spaces in the Property Translation Table file (other than if they exist in the Property Set Key).
-
Use the exact spelling and case for each string in the Property Translation Table file. These have to match the case and spelling used for the PropertySet key (name) in the Sparkplug B birth certificate, and the Geo SCADA Expert Class and Geo SCADA Expert Property Name in the Database Schema. Be aware that British English might be used for some Class and Configuration Field names in the Database Schema.
-
Ensure that you specify the Name (rather than the Display Name) of the Configuration Field in the Database Schema. (The Name does not include any spaces and might also differ in other ways from the Display Name.)
-
Ensure that you only map properties that are of the same or equivalent data type. For example, match a Boolean property in the Sparkplug B birth certificate to the corresponding Boolean configuration field in the Database Schema.
The Type column of a Configuration Field in the Database Schema indicates the property's data type.
-
Do not map to Reference, Index, or Read Only Configuration Fields in the Database Schema. (These are not supported by the Property Translation Table.)
The Notes column of a Configuration Field in the Database Schema includes a 'Read Only' entry if that property is read only.
The Type column in the Database Schema indicates if the Configuration Field is a Reference field. (There are several types of Reference field, including 'AOI Reference' (for Area of Interest Reference fields).)
The Type column also indicates if the Configuration Field is an Index field. (There are several types of Index field, including 'Unique Index'.)
-
Only map to a Configuration Field in the Database Schema. (Property Translation Tables do not support mapping to Data Fields.)
-
Only include entries for configuration properties for which both of the following apply:
-
The values are to differ from the defaults in Geo SCADA Expert
-
You want Geo SCADA Expert to set the values automatically when it creates the points.
Geo SCADA Expert derives the name of each MQTT Sparkplug B Point automatically from the name of the mapped metric in the Sparkplug birth certificate of the EoN Node or Sparkplug B Device.
By default, Geo SCADA Expert automatically selects the In Service check box, and populates the Metric Parent and Metric Name fields on the points that it creates as a result of the Create Points from Birth Metrics pick action (see Configure the Common Point Properties). With any other configuration properties that are omitted from the Property Translation Table file for the EoN Node or Sparkplug B Device, the properties on the points are either left at their default values or left unpopulated (whichever is applicable).
-
-
If an extra (custom) database field exists on any of the MQTT Sparkplug B Point Forms in your Geo SCADA Expert database, you can map a suitable Property Set Key to such a custom configuration field if required.
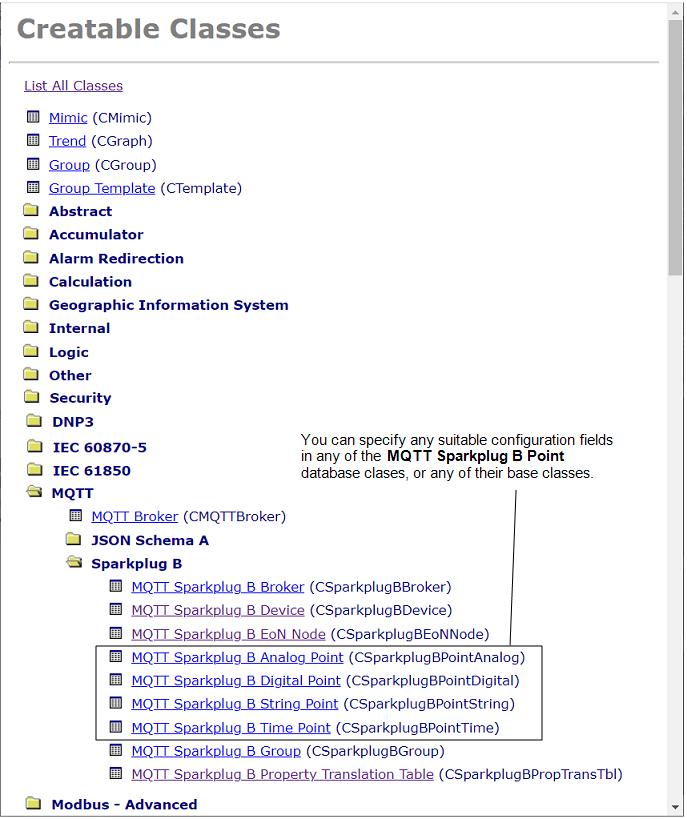
A Property Translation Table is to be used to enable Geo SCADA Expert to automatically configure the following properties on the points that it creates for a particular EoN Node:
-
The description that is to be used for the 'High' limit of the analog points.
-
The description that is to be used for the 'Low' limit of the analog points.
-
The engineering units of the analog points.
-
The description that is to be used for 'State 1' on the digital points.
The Database Schema is used to ascertain the names of the Classes in which the properties are located, along with the names of the Configuration Fields in those Classes:
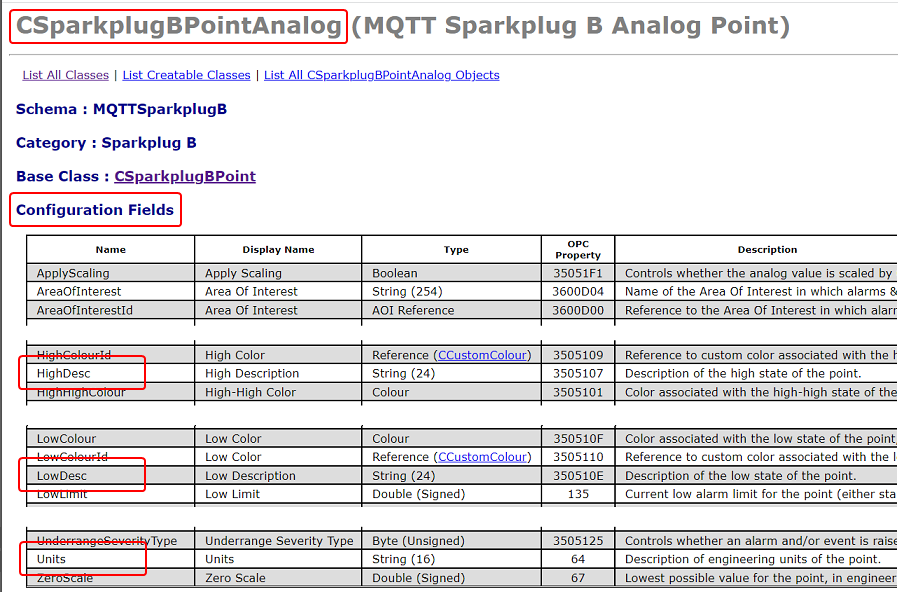
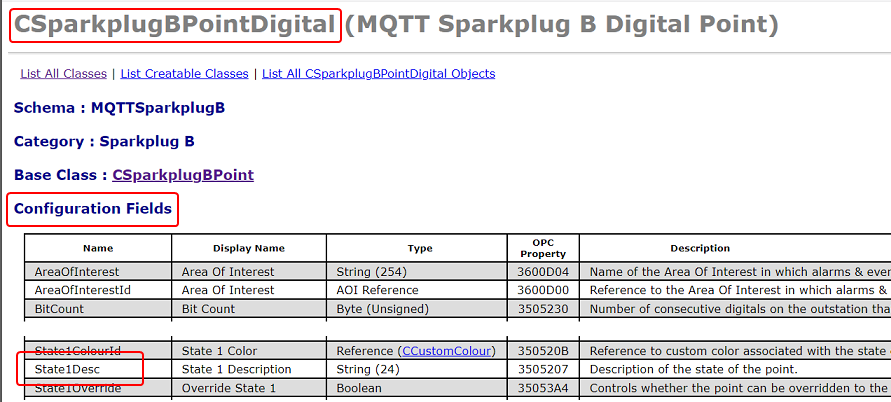
Notice that the Type column specifies the maximum supported string length of each of the properties. Geo SCADA Expert will truncate the strings if they exceed this length when it configures the points.
Also notice that the text in the Name column differs to the text in the Display Name column. It is the text in the Name column that should be included in the TSV file to identify a configuration property.
A TSV file is created to specify that Geo SCADA Expert is to set the values of above 4 configuration properties when it creates the points in the database. The TSV file is used to specify the name of the PropertySet key to which Geo SCADA Expert is to map each configuration property. Each PropertySet key comprises one of the key/value pairs of data that will be included in the Sparkplug birth certificate that Geo SCADA Expert will retrieve for the EoN Node when it first communicates with that EoN Node.
The TSV file comprises just 4 lines (one for each configuration property that Geo SCADA Expert is to set in the database):
AnalHighLimitDesc\tCSparkplugBPointAnalog\tHighDesc\n
AnalLowLimitDesc\tCSparkplugBPointAnalog\tLowDesc\n
MyUnits\tCSparkplugBPointAnalog\tUnits\n
DigStateBDesc\tCSparkplugBPointDigital\tState1Desc\n
With each line, the string to the left of the first horizontal tab (\t) comprises the name of the equivalent PropertySet key that exists for the metric for which Geo SCADA Expert is to automatically create an MQTT Sparkplug B Point in the database. The rest of the string specifies the Class and Configuration Field to which Geo SCADA Expert is to map the PropertySet key. This has to comprise a suitable equivalent configuration field for the Point that Geo SCADA Expert is to create in the database.
So, with the first line:
-
AnalHighLimitDescis the name of a PropertySet key that exists for a metric that Geo SCADA Expert is to map to an MQTT Sparkplug B Analog Point in the database. -
CSparkplugBPointAnalogindicates that Geo SCADA Expert is to map the PropertySet key to a configuration field in the CSparkplugBPointAnalog Class in the database. This is the Class for MQTT Sparkplug B Analog Points. -
HighDescindicates that Geo SCADA Expert is to map the PropertySet key to the HighDesc configuration field in the above Class. This is the configuration property that is used to provide the description of the high state of the analog point.
Once you have produced a suitable Property Translation Table file, you import that file into Geo SCADA Expert. You do this using the Import Property Translation Table pick action on an MQTT Sparkplug B Property Translation Table in the database. For more information, see Use a Property Translation Table to Configure Automatically Created Points.
If the file that is being imported into an MQTT Sparkplug B Property Translation Table in Geo SCADA Expert contains an invalid or unsupported property mapping, that file import will not succeed. Use the Last Import Status attribute to ascertain whether the latest attempt to import a file into a particular Property Translation Table item was successful.
Further Information
Use the Database Schema: see the Geo SCADA Expert Guide to the Database.
Working with the Database Schema.
Understand the Class structure in the Database: see Classes.
Understand the information that is shown about Configuration fields in the Database Schema: see Configuration Fields and Data Fields Section.
Use the Metadata window to create custom extra database fields in Geo SCADA Expert: see Extra Database Fields in the Geo SCADA Expert Guide to Server Administration.