Use the fields on the Channel tab of the appropriate Channel Form to configure the basic communication properties for a channel.
The following fields are displayed for channels on many advanced drivers:
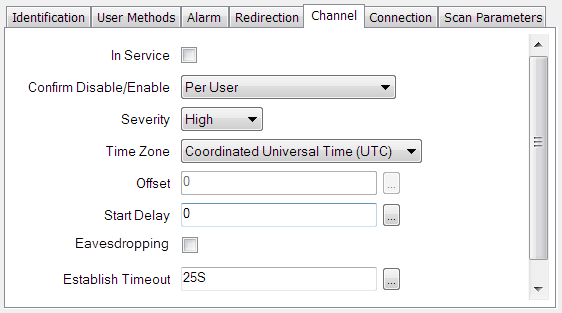
Use to specify whether the channel is active or inactive (see Placing an Item In Service).
The ClearSCADA server only communicates via channels that are enabled and are therefore ‘In Service’.
With some setups, a channel might be the sole means by which ClearSCADA communicates with certain devices. If you take such a channel out of service, the database items that represent those devices will also become out of service (although their configuration will remain unchanged).
Users with the required permissions can disable a channel that is In Service, or enable a channel that is not In Service. Such actions are performed using the Disable Channel and Enable Channel pick actions.
Use the Confirm Disable/Enable combo box to specify whether a confirmation dialog box is displayed whenever an operator requests that this channel is disabled or enabled (see Requesting Confirmation of Action Requests).
You use the Disable Channel pick action to take a channel out of service. If that channel is the sole means by which ClearSCADA communicates with certain devices, taking that channel out of service will also de-activate the database items that represent those devices.
Use the combo box to define the priority of any alarms or events that are associated with the channel (see Defining Severities).
If the Area of Interest feature is enabled on your system, an additional Area of Interest field is displayed on the Channel tab. Use the field to specify the area with which any of the channel’s alarms or events are to be associated (see Assign a Different Area of Interest to an Item’s Alarms and Events).
For further information on the Area of Interest feature, see Restrict Alarm and Event Access to Specific Areas of Interest.
Use the combo box to specify the time zone that is used by the outstations’ clocks on this channel. The options vary, depending on the driver, but include one or more of the following:
The clocks run in Coordinated Universal Time.
When you select this option, it activates the Offset option that appears below it. This allows you to offset (add or subtract) a fixed amount of time from UTC.
The clocks run in Local Time, for instance EST (Eastern Standard Time) if the local time zone is that for the East coast of America. No adjustments are made for Daylight Saving Time (DST).
The clocks run in Local Time. ClearSCADA automatically adjusts the time to account for Daylight Saving Time.
ATTENTION: Depending on the driver, there may be gaps in the data when the clocks are adjusted forwards, or missing data when times repeat after the clocks are adjusted back to account for DST. Use the Local Time without Daylight Saving Time option if such gaps are not acceptable on your system.
On drivers that support local time but not daylight saving time, the latter two options are replaced by a single Local Time option.
For more information, see Time Zone Support in ClearSCADA.
Specify the amount of time between system start-up and the initial availability of the channel. The ClearSCADA server cannot use the channel for communications until the Start Delay time has expired.
Set the Start Delay to 0 on channels on which no delay is required between the system starting up and the channel being available for use. This is the default setting.
Set the Start Delay to a suitable value greater than 0 on channels on which a delay is required between the system starting up and the channel being available for use. For example, on a PSTN channel that is used as a dial-in PSTN fallback channel on outstations that support PSTN fallback. By entering a suitable Start Delay, you allow time for the ClearSCADA server to attempt to establish direct communications with the outstation, before ‘falling back’ to the PSTN channel. If you do not define such a Start Delay, the PSTN channel can be used instead of the direct communications, even when the direct channels are ‘Healthy’—the PSTN channel should only be used when the ClearSCADA server cannot establish communications via the direct channels.
If a PSTN channel is used as a ‘fallback’ channel, specify a suitable Start Delay. We recommend that you use the Event Journal (Events List) to determine how long it takes for the system to start direct communications with each outstation. You should set the Start Delay so that it is greater than the longest time taken to establish direct communications with any outstation that can use the PSTN channel.
You might also want to specify a suitable Start Delay should your system, for example, use multiple channels that communicate via a satellite link. With such a setup, consider whether you want to offset the start-up time of some of the channels to help prevent the satellite links from becoming saturated, should numerous channels activate simultaneously in the event of the system or driver being restarted.
In each case, enter a suitable Start Delay in the OPC Time Format. For example, 20S for 20 seconds. You can enter the value directly in the field, or use the Interval Window (accessed via the field’s browse button) to specify the required delay.
If a channel is not used as a PSTN ‘fallback’ channel and a start-up delay is not required for other reasons, set the Start Delay to 0.
Only displayed if supported by the driver. Eavesdropping is designed for use when upgrading a system. You can use eavesdropping to allow a ClearSCADA server to receive unsolicited data via a serial cable link with a channel used by another server.
Use the check box to define whether eavesdropping is enabled or disabled. The check box displays a check mark when eavesdropping is enabled.
You should only enable eavesdropping if the communications channel is connected to the older server’s Rx connection (input connection), or Tx connection (output connection), as required by the protocol. Some protocols require both Tx and Rx eavesdropping, in which case a separate port is needed for each connection. For those drivers that support eavesdropping, the driver-specific documentation indicates which eavesdropping connection(s) are required by that protocol.
For more information on eavesdropping, see Using Eavesdropping to Test a New Server’s Configuration.
Specify the maximum permitted amount of time that can elapse between an incoming connection being made and ClearSCADA establishing communications with the outstation via this channel. With Direct channels, the timeout applies to inbound network connections; with PSTN channels, the timeout applies to calls made by an outstation dialing in to ClearSCADA.
In either case, if the outstation does not respond within the defined time, the ClearSCADA server cannot establish communications with the outstation and so deems the connection or call to have failed. The failure is shown in the statistics for the channel and the outstation (see the driver-specific documentation).
Specify the timeout in the OPC Time Format, for example, 25S for 25 seconds. You can enter the value directly in the field, or use the Interval Window (accessed via the field’s browse button) to specify the required time.