Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is a universally recognized time standard that is based on International Atomic Time (TAI). With UTC, leap seconds are added at irregular intervals to maintain the time’s accuracy in relation to the Earth’s slowing rotation. UTC replaced Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) as the main reference time standard used by many regions worldwide in January 1972.
With UTC, there are no time adjustments in relation to Daylight Saving Time.
Local Time zones around the world can be expressed as positive or negative offsets from UTC.
The Network Time Protocol (NTP)—an Internet protocol used for synchronizing the system clocks on many computer systems—uses UTC to synchronize such clocks. The protocol synchronizes the clocks to the time of a ‘reference’ clock, such a known accurate atomic clock.
ATTENTION: This note only applies to machines that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 or earlier versions of Windows. With such versions of Windows, the W32Time service is not a full-featured NTP solution. Therefore, for high accuracy environments (such as ones in which time needs synchronizing to within an accuracy of 1 to 2 seconds), use an NTP client to maintain accurate time, and disable Windows Time (W32Time).
Windows Time uses the Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP), which is a simplified version of Network Time Protocol (NTP). As such, high accuracy tolerances such as that mentioned above are outside of the design specification of the W32Time service. For more information,
(With computers that are running Windows Server 2016 and newer operating system versions, high accuracy time can be achieved using W32Time, providing that certain criteria are satisfied. For more information,
Internally the ClearSCADA server processes and stores time values in UTC. With any feature or function that runs in Local Time and with which ClearSCADA interacts, ClearSCADA converts the time from UTC to Local Time as required (see Time Zone Support in ClearSCADA).
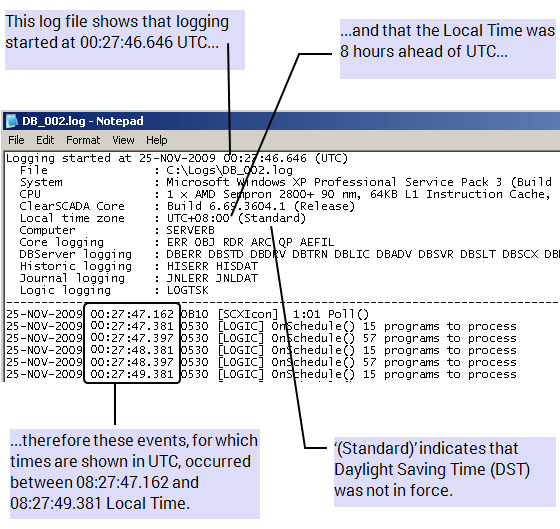
Any log files generated by ClearSCADA show time values in UTC. The log file header indicates the Local Time zone that applied at the time that the log file was generated. The Local Time zone is shown as an offset from UTC, enabling you to ascertain when a particular activity occurred in either UTC or Local Time.
Example:
On some systems, ClearSCADA’s Automation Interface is used to enable external applications to query items in the ClearSCADA database. The Automation Interface provides time values in UTC. Should time values be required in Local Time, the external application or a third-party program will need to convert the time values from UTC to Local Time. For further information see Server Automation.
With external applications that query items in the ClearSCADA database using ODBC, you can specify whether the third party ODBC Client converts the time values supplied by ClearSCADA from UTC to Local Time (see Configure an ODBC Client - System Connection using a DSN).